The Versatility of Pregabalin 75 mg: A Solution for Neuropathic Pain, Epilepsy, and Anxiety
Introduction
Pregabalin, marketed under the brand name Lyrica, is a medication that has garnered significant attention for its versatility in treating various conditions, particularly neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and anxiety disorders. Approved by regulatory bodies across the globe, pregabalin has become a staple in the therapeutic arsenal for managing these challenging health issues. This article explores the multifaceted applications of pregabalin 75 mg, shedding light on its mechanism of action, efficacy, side effects, and the broader implications of its use.
Understanding Pregabalin
Pregabalin is an analog of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it primarily binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. This action inhibits excitatory neurotransmitter release, which is crucial for managing pain signals and seizure activity. Pregabalin was first approved in the early 2000s and has since evolved as a first-line treatment for several conditions.
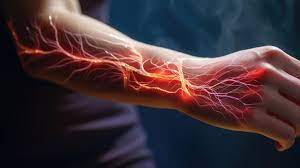
Pregabalin 75 mg Capsule is used to treat pain that results from damage to the nerves (neuropathic pain), which can be brought on by diabetes, shingles (herpes zoster infection), spinal cord injuries, or other ailments. It is also utilized to alleviate fibromyalgia patients’ diffused muscle soreness and stiffness. Side effects of pregabalin are anxiety, dizziness, headache, Difficulties with articulation, An absence of cohesion and A bloated feeling of euphoria etc.
Mechanism of Action
Pregabalin’s mechanism of action is particularly important in understanding its versatility. By modulating calcium channels, pregabalin decreases the influx of calcium ions into neurons. This inhibition reduces the release of several neurotransmitters, including glutamate, substance P, and norepinephrine, which play pivotal roles in pain perception, seizure activity, and anxiety responses. Consequently, pregabalin effectively reduces pain, stabilizes neuronal excitability, and alleviates anxiety symptoms.
Pregabalin for Neuropathic Pain
Overview
Neuropathic pain arises from damage or dysfunction in the nervous system, leading to abnormal pain signals. Conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and spinal cord injury are common causes. This type of pain is often chronic and can significantly impair quality of life.
Efficacy
Pregabalin has been extensively studied for its effectiveness in treating neuropathic pain. Research indicates that doses ranging from 75 mg to 600 mg per day significantly reduce pain levels. A systematic review published in “The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews” found that pregabalin is more effective than placebo in alleviating neuropathic pain, with many patients experiencing a notable reduction in pain intensity within a few weeks of treatment.
Dosage and Administration
The starting dose of pregabalin for neuropathic pain is typically 75 mg once or twice daily, which can be adjusted based on individual response and tolerability. Clinicians often increase the dosage incrementally, allowing patients to achieve optimal pain control while minimizing side effects.
Side Effects
While pregabalin is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects, including dizziness, fatigue, and dry mouth. Serious side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions and suicidal thoughts. Monitoring patients, particularly those starting on the medication, is crucial to managing these risks.
Pregabalin in the Treatment of Epilepsy
Overview
Pregabalin is also indicated for the treatment of partial seizures in adults. Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, which can be debilitating and socially stigmatizing.
Efficacy
Clinical trials have shown that pregabalin significantly reduces seizure frequency in patients with epilepsy. A study published in “Epilepsia” demonstrated that patients treated with pregabalin experienced a greater reduction in seizure frequency compared to those on placebo. The drug can be used as monotherapy or in conjunction with other antiepileptic drugs, providing flexibility in treatment plans.
Dosage and Administration
For epilepsy, pregabalin is typically initiated at 75 mg twice daily, with the potential for upward titration based on the patient’s response. The flexibility of dosage allows for individualized treatment, accommodating varying levels of seizure control and tolerability.
Side Effects
Similar to its use in neuropathic pain, the side effects of pregabalin in epilepsy treatment are generally manageable. However, patients must be educated about potential impacts on cognitive function, including dizziness and drowsiness, especially when combined with other antiepileptic medications.
Pregabalin for Anxiety Disorders
Overview
Pregabalin has gained recognition for its efficacy in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Anxiety disorders are among the most prevalent mental health conditions, often leading to significant functional impairment.
Efficacy
Clinical evidence supports the use of pregabalin for GAD, with studies indicating a rapid onset of action compared to traditional anxiolytics like benzodiazepines. A meta-analysis published in “Psychological Medicine” highlighted that pregabalin effectively reduces anxiety symptoms, with many patients reporting improvement within the first week of treatment.
Dosage and Administration
For anxiety, the typical starting dose is also 75 mg per day, which can be adjusted based on clinical response. The ease of titration allows healthcare providers to personalize treatment, considering factors such as patient history and symptom severity.
Side Effects
The side effect profile for pregabalin in anxiety treatment mirrors that of its other indications. Patients may experience sedation, weight gain, or cognitive effects. Proper education about these potential side effects can help manage patient expectations and improve adherence to treatment.
Considerations for Use
Tolerability and Patient Adherence
One of the key advantages of pregabalin is its tolerability profile. Unlike some traditional pain medications and anxiolytics, pregabalin has a lower potential for abuse and dependence, making it a favorable choice for long-term management. This aspect is particularly important in patients with a history of substance use disorder.
Drug Interactions
Pregabalin can interact with other medications, especially central nervous system depressants. Therefore, healthcare providers should review patients’ medication lists thoroughly to avoid complications. Patients should be advised to inform their healthcare providers of any other medications, supplements, or herbal products they are taking.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments are essential for patients on pregabalin, allowing for ongoing assessment of efficacy, side effects, and the need for dosage adjustments. Monitoring can also help identify any emerging concerns, such as mood changes or signs of misuse.
The Broader Implications of Pregabalin Use
Economic Impact
The use of pregabalin can have a significant economic impact on healthcare systems. By effectively managing conditions like neuropathic pain and anxiety, pregabalin may reduce the overall burden of chronic diseases, leading to fewer hospitalizations and a decrease in healthcare costs.
Quality of Life
Pregabalin’s ability to alleviate pain, stabilize seizure activity, and reduce anxiety symptoms directly contributes to improved quality of life for patients. Enhanced physical and mental well-being can lead to greater participation in daily activities and an overall increase in life satisfaction.
Future Research Directions
While pregabalin has proven benefits, ongoing research is essential to explore its full potential. Studies investigating its effects in different populations, long-term safety, and comparative efficacy with newer agents will continue to shape the understanding of pregabalin’s role in therapy.
Conclusion
Pregabalin 75 mg represents a versatile solution in the management of neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and anxiety disorders. Its unique mechanism of action, coupled with a favorable side effect profile, positions it as a valuable therapeutic option for patients suffering from these challenging conditions. As research advances and clinical experience grows, pregabalin will likely continue to play a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.