How is skin cancer of the ear treated?
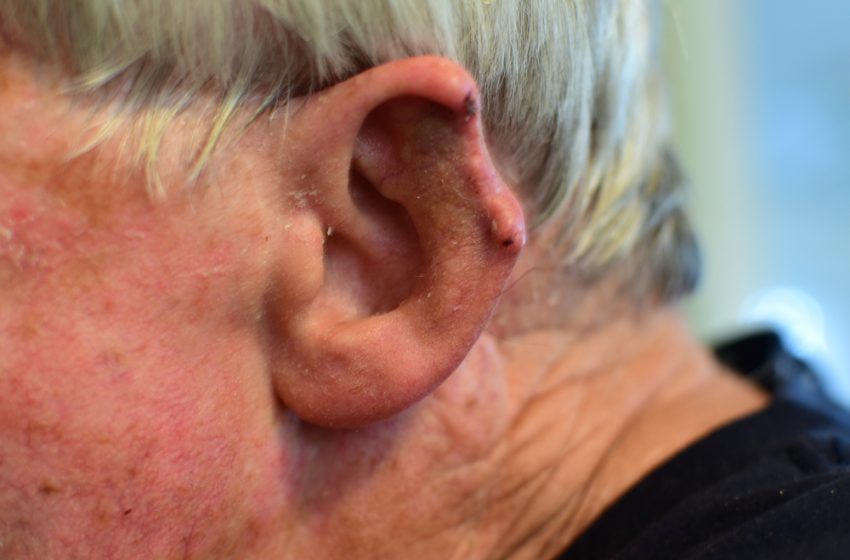
Skin cancer is the most common form that can appear anywhere on the skin, including the ears. It is a type of cancer that develops on the outer side of the ear; once it develops, it grows uncontrollably. Ear cancer starts in the outer ear and spreads throughout various ear structures. As the ear is one of the prominent features of the skin, being affected with cancer not only leads to other health problems but even makes you irritable most of the time.
However, in this blog, we will explore what skin cancer is and the areas that are most likely to develop. We will also list down the best treatment for skin cancer on ear.
Understanding Ear Cancer
When your skin gets excessive exposure to the sun’s UV rays, it gets affected. This is a rare type of cancer that starts within the ear. It can affect both the outer and inner sides of the ear. More than 300 people in the United States are diagnosed with it every year. Most skin cancer cases are easily treated but spread if left untreated. However, it starts affecting the ear’s bone, called the temporal bone. This bone also includes the mastoid bone, which results behind the ear. Moreover, ear cancer develops with red patches, sores, and lumps. Ultimately, we can distinguish skin cancer based on their types, which are listed below:
Basal Cell Carcinoma:
The most common type of cancer is basal cell carcinoma, it appears as a small, pearly bump that doesn’t sore but does not even heal.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
It is an aggressive type of cancer that looks like a scaly patch or ulcerated lesion.
Melanoma:
It is the least common type but is quite severe, it is characterized by dark or irregularly shaped spots.
Causes of Ear Cancer
The primary care for ear cancer is exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight. Moreover, other factors include:
- Chronic Infection
- Genetic Predispositions
- Exposure to substances like industrial chemicals.
- History of skin cancer in any other body parts.
How skin ear cancer is diagnosed
Diagnosis of skin cancer involves several steps to identify its types and stages:
- Physical Examination- Your dermatologist will inspect your infected areas and look for malignant signs.
- Biopsy-Take a sample for microscopic analysis to confirm cancer.
- Imaging Tests- Like CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds to analyze any cancer present nearby.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the chances of developing ear cancer; these factors are:
- Prolonged sun exposure.
- Use of tanning beds.
- Fair skin, hair, and light eyes.
- A history of severe sunburn.
- Weak immune systems.
- A family history of skin cancer.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
-
The symptoms of skin cancer include:
- Discolored skin
- Itching or bleeding
- Pink lumpy surface
- Yellow or white scars
- The irregular shape of a mole
- Hard to distinguish
- Multiple colored mole
Essential Treatment for Ear Cancer
Skin cancer is one of the common forms of cancer, and it can occur anywhere on the skin, including the ears. Ears are at high risk due to their exposure to the sun. Treatment of ear cancer generally depends on the size of the cancerous growth and where it is located. However, skin cancer on the outer side of the ear is generally cut out; large areas are removed with the help of reconstruction surgery. Moreover, for ear canal or temporal bone cancer, radiation surgery is required. In some cases, the ear canal, ear bone, and ear drum have to be removed depending on the nature of your tumor.
Types of Treatment Options for Outer Ear Cancer
There are various remedial measures including surgical operation or radiation therapy, and more. However, these measures almost cure cancers in the external portion of the ear. Moreover, the category and extent of surgery depend on various conditions. The most common types of surgery are listed below:
- Mohs micrographic surgery
- Excisional biopsy
- Lymph node dissection
- Wide Local Excision
- Otoplasty
Mohs Micrographic Surgery
In this surgery, thin layers of cancer-containing skin are removed along with the surrounding layer of healthy tissues. Moreover, the thin layer of cancer found on the skin which has been removed through Mohs surgery, is subjected to staining, sectioning, freezing, and mapping in detail. A layer-by-layer removal technique, allowing precise excision with minimal tissue loss. It is ideal for cancers in sensitive areas like the ear. Lastly, it is then examined under a microscope.
Wide Local Excision
The procedure of wide local excision generally exercises 1 to 2 cm of healthy skin layer around the melanoma surface. In addition to the initial biopsy, wide local excision is used in melanomas. Nevertheless, variation in this margin depends on factors such as the impact of tumor depth and its extent of spread into the dermis and hypodermis layers of the skin. Closing the wide local excision with stitches is often performed on smaller lesions, but skin grafts or skin flaps may be employed on larger lesions.
Excision Biopsy
In an excision biopsy approach, the surgeon uses a lancet to completely excise the entire tumor-affected region and excision the margin of healthy skin around it. The surgical wound around the tumor site may be stitched up. This is the removal of cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy skin. It is best for small to medium-sized cancers.
Lymph Node Surgery
In lymph node biopsy, the lymph node tissue is examined under a microscope to identify the symptoms of a tumor or other infection. Moreover, the lymph nodes are listed under the human immune system. However, it is present everywhere across the body, but swollen lymph nodes are found in the neck, armpits, and groin area and can be easily identified.
Otoplasty or Ear Reconstruction Surgery
Ear reconstruction is also known as otoplasty which is one of the complex areas of plastic surgery. Firstly, reconstructive surgery develops a skin patch at the location of the tissue by matching the ascetics of skin layer.
Radiotherapy
In radiotherapy, high-quality rays are implemented to treat cancer. To start with radiation treatment, the patient has to consult with the radiologist to plan a treatment schedule, which can last between 4 and 6 weeks. In this procedure high-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells, this is used for larger types of cancers.
Living with Ear Cancer
Living with ear cancer makes you attend regular check-ups to monitor for recurrence. You also have to cope with physical, emotional, and psychological adjustments. Moreover, you need to protect your skin, use sunscreen to prevent further damage. However, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking to promote overall wellness to get used to living with ear cancer.
Read Also: what are symptoms of normocytic anemia?
Summary
Skin cancer of the ear is a serious condition but is treatable, especially when detected early. It involves risk factors due to sun exposure and can be managed with preventive measures, including sunscreen. Moreover, skin cancer on the ear can involve thorough examination and biopsy, followed by customized treatment options such as surgery, radiation, or immunotherapy.
Ear cancer requires lifestyle changes and ongoing medical care, but with early intervention and innovative treatment options, one can recover and have an improved quality of life. If you notice any unusual changes in the skin of your ear, consult the Primary Care Clinic in Bedford for immediate evaluation and care.

