Diagnostic Approaches: How Healthcare Professionals Identify Neuropathic Pain
In this article, we delve into the diagnostic approaches used by healthcare professionals to identify neuropathic pain accurately. Additionally, we explore the role of medications like Pregabalin 150 mg in managing neuropathic pain and providing relief.
Understanding Neuropathic Pain
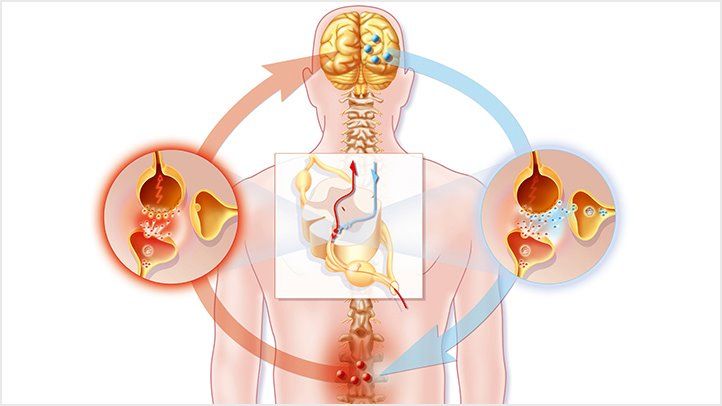
Neuropathic pain stems from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system, leading to abnormal nerve signaling and persistent pain sensations. Unlike nociceptive pain, which arises from tissue damage, neuropathic pain is often characterized by shooting, burning, or tingling sensations that may persist beyond the healing process.
Clinical Assessment
Healthcare professionals conduct a comprehensive clinical assessment to evaluate patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of neuropathic pain. This assessment includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and evaluation of presenting symptoms. Patients may describe sensory abnormalities such as tingling, numbness, or hypersensitivity, along with spontaneous or evoked pain sensations.
Neurological Examination
A neurological examination is a critical component of diagnosing neuropathic pain. Healthcare professionals assess sensory function, motor strength, reflexes, and nerve function to identify abnormalities indicative of neuropathy or nerve damage. Tests such as pinprick sensation, light touch, temperature perception, and proprioception evaluation help elucidate sensory deficits associated with neuropathic pain.
Diagnostic Testing
Diagnostic testing may be employed to confirm the presence of neuropathic pain and identify underlying etiologies. Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) assess nerve function and detect abnormalities in nerve conduction velocity or muscle response, indicative of peripheral neuropathy or nerve damage. Imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be utilized to visualize anatomical structures and identify structural abnormalities compressing or injuring nerves.
Diagnostic Criteria
Various diagnostic criteria and scoring systems, such as the Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs (LANSS) and the Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire (NPQ), help healthcare professionals classify and quantify neuropathic pain symptoms. These tools incorporate patient-reported symptoms, sensory abnormalities, and clinical examination findings to establish the likelihood of neuropathic pain.
Role of Medications
Medications like Pregabalin 150 mg play a pivotal role in managing neuropathic pain by modulating abnormal nerve signaling and reducing pain transmission. Pregabalin, an anticonvulsant medication, binds to voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, inhibiting the release of neurotransmitters involved in pain processing. It is effective in relieving neuropathic pain symptoms and improving patient function and quality of life.
Multimodal Approach
Treatment of neuropathic pain often necessitates a multimodal approach that combines pharmacological interventions with non-pharmacological therapies. In addition to medication, interventions such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and nerve blocks may be utilized to manage pain, improve function, and address psychosocial aspects of neuropathic pain.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis of neuropathic pain requires a systematic approach encompassing clinical assessment, neurological examination, diagnostic testing, and utilization of validated diagnostic criteria. Medications like Pregabalin 150 mg offer effective relief for neuropathic pain symptoms and play a crucial role in pain management. By employing a comprehensive diagnostic approach and integrating multimodal treatment strategies, healthcare professionals can effectively identify and manage neuropathic pain, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare professionals employ various methods to identify neuropathic pain accurately. A comprehensive clinical assessment begins with a detailed medical history, where patients describe their symptoms, including the nature, location, intensity, and duration of pain. Understanding the temporal pattern of symptoms and any associated factors, such as prior injuries or medical conditions, provides valuable insights into the underlying etiology of neuropathic pain.
The physical examination focuses on neurological assessment, evaluating sensory function, motor strength, reflexes, and coordination. Sensory testing, including assessment of light touch, temperature perception, and pinprick sensation, helps detect abnormalities indicative of neuropathy or nerve damage. Reflex testing and muscle strength assessments aid in identifying neurological deficits associated with neuropathic pain.
Diagnostic testing complements the clinical assessment and may include nerve conduction studies (NCS), electromyography (EMG), and imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. NCS and EMG evaluate nerve function and muscle response, identifying abnormalities in nerve conduction velocity or muscle activity suggestive of peripheral neuropathy or nerve compression. Imaging studies provide detailed anatomical information, helping identify structural abnormalities or lesions affecting nerve pathways.
Validated diagnostic criteria and scoring systems, such as the Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire (NPQ) and the Douleur Neuropathique en 4 Questions (DN4), aid in the classification and quantification of neuropathic pain symptoms. These tools incorporate patient-reported symptoms and clinical examination findings, assisting healthcare professionals in establishing the likelihood of neuropathic pain and guiding treatment decisions.
Treatment Modalities
Medications like Pregabalin 150 mg are integral components of neuropathic pain management. Pregabalin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, exerts its therapeutic effects by binding to voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, modulating neurotransmitter release and reducing aberrant neuronal excitability. By inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate, pregabalin attenuates pain transmission and alleviates neuropathic pain symptoms.
Non-pharmacological interventions complement pharmacotherapy and may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and psychological interventions. Physical therapy modalities such as exercise, stretching, and manual techniques aim to improve mobility, reduce muscle tension, and enhance functional capacity. Occupational therapy focuses on enhancing activities of daily living (ADLs) and promoting independence through adaptive strategies and assistive devices.
Psychological interventions, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), address the emotional and psychological aspects of neuropathic pain. These therapies help individuals develop coping mechanisms, manage stress, and improve their overall quality of life by fostering resilience and promoting adaptive coping strategies.
Multimodal Approach
A multimodal treatment approach that integrates pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions offers the most comprehensive and effective management of neuropathic pain. Treatment plans are individualized based on the patient’s clinical presentation, underlying etiology, comorbidities, and treatment goals.
Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential to assess treatment response, adjust medication dosages, and address any emerging concerns or complications. Patient education and empowerment play a crucial role in promoting self-management strategies and fostering active participation in the treatment process.