Useful Advice for Preventing Hives Triggers
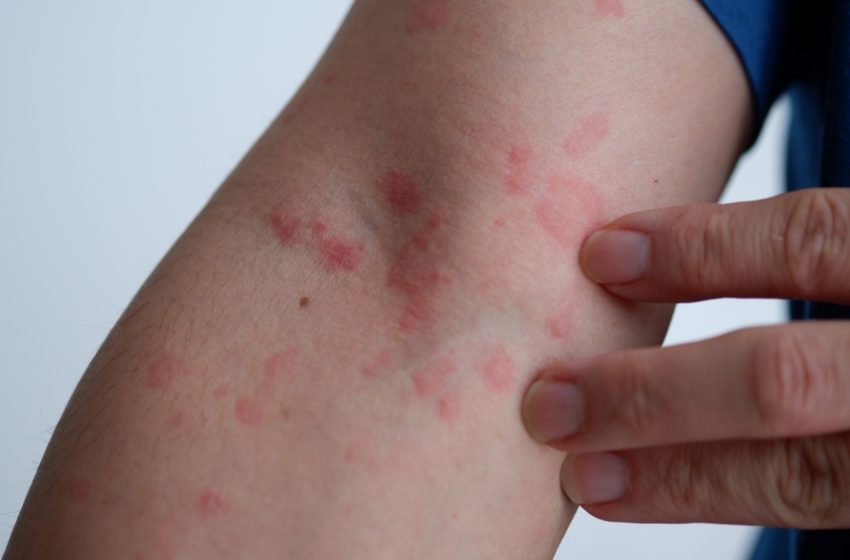
Hives, medically known as urticaria, are red, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body, varying in size and shape. These welts often have a red or pink tint and can sometimes merge to form larger areas of irritation. The itching associated with hives can range from mild to severe and can last from a few hours to several days. Hives are typically a reaction to an allergen or irritant, causing the skin to release histamine, a chemical that leads to swelling and irritation.
While many cases of hives resolve on their own, recurrent or chronic hives can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to discomfort and anxiety. Understanding the underlying causes and triggers of hives is essential for effective management and prevention strategies.
Common Triggers of Hives
Hives are commonly triggered by various allergens and environmental or physical factors. Understanding these triggers is crucial in managing and preventing hives. Some of the most common hives triggers include:
Food Allergens
- Certain foods are frequent culprits for hives outbreaks. Common food triggers include nuts, shellfish, dairy products, eggs, and soy. When the body mistakenly identifies these foods as threats, it releases histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream, causing hives.
- Individuals with known food allergies should be cautious with their diet.
Environmental Factors
- Environmental allergens such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold can lead to hives. For individuals sensitive to these substances, exposure can trigger an immune response that results in skin irritation.
- Seasonal changes can also influence hives, especially for those allergic to pollen or other plant-based allergens. Maintaining a clean home environment and using air purifiers can help manage these triggers.
Physical Factors
Physical elements like temperature and pressure changes can also provoke hives. Common physical triggers include:
- Heat: Excessive heat, sweating, or sudden temperature changes can prompt hives, especially in people with a condition called cholinergic urticaria.
- Cold: Cold urticaria is a form of hives triggered by exposure to cold weather, cold water, or even cold food.
- Pressure: Tight clothing, heavy bags, or prolonged sitting/standing can cause pressure-induced hives, where welts develop on the skin in areas where pressure was applied.
Medications
- Certain medications can cause hives in some individuals. This reaction may be due to an allergy or sensitivity to a particular drug, leading to an immune response and histamine release.
- It’s essential for those who experience medication-induced hives to consult with their healthcare provider to find safe alternatives if necessary.
Tips to Prevent Hives Triggers
Taking steps to manage potential triggers of hives can significantly reduce the likelihood of flare-ups. Below are practical strategies for handling common hive triggers effectively.
Managing Food Allergens
-
Reading Food Labels Carefully
- Many processed foods contain hidden allergens, so it’s important to check labels for common allergens like nuts, shellfish, and dairy. Even trace amounts can sometimes trigger hives.
- Watch out for ingredients that may be listed under different names or in unexpected places.
-
Avoiding Cross-Contamination in Meal Preparation
- When preparing food at home, cross-contamination can occur if utensils, cutting boards, or surfaces come in contact with allergens. Designate separate utensils and surfaces when possible, especially when handling common allergens like nuts or shellfish.
- In restaurants, ask about potential cross-contact risks, especially if you have severe allergies. Many places now have allergy menus or can provide extra precautions in the kitchen.
-
Keeping an Emergency Plan in Place for Accidental Exposure
- If you have severe allergies that could lead to hives, it may be helpful to carry an epinephrine injector for emergencies.
- Make sure friends, family members, or coworkers are aware of your allergies and know what to do if you have an allergic reaction.
Controlling Environmental Factors
-
Using Air Purifiers to Reduce Allergens
- Air purifiers with HEPA filters can help remove airborne allergens like pollen, pet dander, and dust, which can reduce the likelihood of hives in those sensitive to environmental triggers.
- Keep windows closed during high pollen seasons and change air filters in your home regularly.
-
Keeping Pets Clean and Well-Groomed
- Pet dander can trigger hives for those with sensitivities. Regularly bathing and grooming pets can help reduce the amount of dander they shed.
- Designate certain rooms as pet-free zones, especially bedrooms, to reduce overall exposure to allergens.
-
Regularly Cleaning Home Surfaces
- Dust mites and other allergens can accumulate on surfaces over time, so it’s important to regularly clean floors, furniture, and bed linens.
- Wash bedding frequently in hot water to kill dust mites and consider using dust mite-proof pillows and mattress covers.
Managing Physical Factors
-
Dressing in Layers to Regulate Body Temperature
- Temperature changes, particularly excessive heat or cold, can trigger hives in some individuals.
- Lightweight, breathable fabrics can also help keep skin cool and dry, reducing the risk of sweat-induced hives.
-
Avoiding Tight Clothing to Reduce Pressure on Skin
- Tight clothing or accessories that put pressure on the skin can sometimes lead to pressure-induced hives. Opt for loose, comfortable clothing that doesn’t irritate the skin or restrict circulation.
- Avoid wearing heavy bags or other items that apply prolonged pressure to specific areas.
The Importance of Clinical Trials in Advancing Urticaria Treatments
Clinical trials are crucial in advancing medical knowledge and developing new treatments for various health conditions. They allow researchers to test the safety and effectiveness of novel therapies, ensuring that any new medications or procedures meet rigorous standards before becoming widely available. For patients, clinical trials can offer access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to better health outcomes for future patients. In the case of chronic skin conditions like urticaria, trials are essential for exploring innovative therapies that might provide relief where current treatments fall short. Those who participate in urticaria clinical trials not only help drive progress in dermatological research but may also benefit from potential new treatments under expert supervision.
What is Papular Urticaria?
Papular urticaria is a common skin reaction, especially in children, triggered by insect bites such as those from mosquitoes, fleas, or bedbugs. It causes itchy, red and raised bumps on the skin, which can sometimes lead to blistering or secondary infections if scratched excessively. Unlike other types of hives, papular urticaria often lasts longer and can recur when the individual is exposed to similar insect bites. To manage papular urticaria, it’s essential to reduce exposure to insects through protective measures like using insect repellents, wearing long clothing, and keeping living areas clean. Treatment often includes topical antihistamines or corticosteroids to relieve itching and inflammation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the triggers and management strategies for hives is essential for those affected by this uncomfortable skin condition. By identifying common allergens—such as certain foods, environmental factors, and medications—individuals can take proactive steps to minimize exposure and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Moreover, exploring treatment options through clinical trials can pave the way for innovative therapies that enhance quality of life. Engaging in clinical trials not only supports personal health but also contributes to the broader understanding of urticaria, ultimately helping countless others who struggle with this condition. By taking these preventive measures and remaining informed, individuals can better navigate their experiences with hives and improve their overall well-being.

