How Gas Turbines Are Transforming the Future of Energy Production
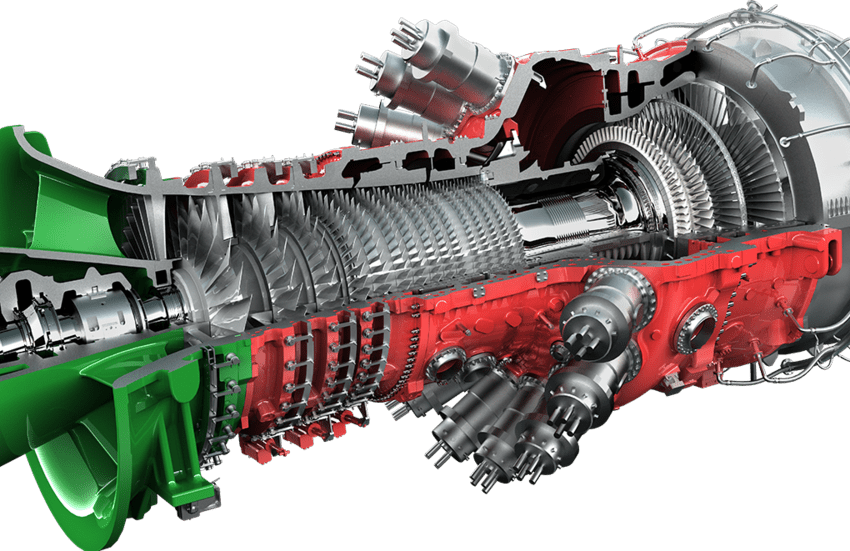
Gas turbines have long been a cornerstone in the world of energy production. Initially developed for aviation, they have evolved to become major in the generation of power. As the global energy landscape shifts toward cleaner and more flexible solutions, gas turbines are taking on an increasingly important role. Their ability to generate power efficiently, with lower emissions than traditional fossil fuel methods, makes them a valuable asset in the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
How Gas Turbines Work
At their core, gas turbines operate on a simple principle: they convert energy from fuel into mechanical energy, which is then used to generate electricity. The process begins with the compressor, which draws in and pressurizes air. The pressurized air is then mixed with fuel in the combustor, where it is ignited to create hot gasses. These gasses expand rapidly and pass through the turbine section, causing it to spin. This mechanical energy drives a generator, producing electricity.
Gas turbines are known for their high efficiency, especially when used in combined cycle power plants, where they work alongside steam turbines to generate even more power from the same fuel.
The Role of Gas Turbines in Power Generation
Gas turbines are widely used in power plants, particularly in combined cycle plants. In this configuration, a gas turbine generates electricity, and the waste heat it produces is used to power a steam turbine, maximizing efficiency. This setup can achieve efficiency levels of over 60%, making it one of the most efficient ways to generate electricity today.
Compared to traditional coal-fired power plants, gas turbines offer a much cleaner alternative. They emit far fewer pollutants, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulphur dioxide. Additionally, gas turbines can be ramped up or down quickly, making them ideal for balancing the grid, especially as renewable energy sources like wind and solar become more prevalent.
Innovations in Gas Turbine Technology
In recent years, significant innovations have propelled gas turbine technology forward. One major area of advancement is in turbine efficiency. Engineers are constantly working to design turbines that can operate at higher temperatures, which improves their efficiency. This requires the use of advanced materials and cooling systems to withstand extreme conditions inside the turbine.
Digitalization is also revolutionizing gas turbine performance. Modern turbines are equipped with smart sensors that monitor performance in real-time, allowing operators to optimize efficiency and anticipate maintenance needs before issues arise. This predictive maintenance reduces downtime and extends the life of the turbine.
Gas Turbines and Renewable Energy Integration
As the world increasingly embraces renewable energy, gas turbines are playing a critical supporting role. Wind and solar power are inherently intermittent—they depend on weather conditions and the time of day, meaning they cannot always provide a steady supply of electricity. Gas turbines, however, can be brought online quickly to compensate for any shortfalls in renewable energy generation, ensuring a reliable power supply.
In some cases, gas turbines are used in hybrid power plants, where they work in tandem with renewable energy sources and battery storage systems. This combination ensures that power can be generated sustainably and reliably, even when renewable sources are not available.
Environmental Impact of Gas Turbines
One of the main advantages of gas turbines is their ability to generate power with relatively low carbon emissions. While they still rely on fossil fuels, gas turbines produce significantly less carbon dioxide than coal plants. Moreover, there is ongoing research into hydrogen-fuelled gas turbines, which could potentially operate with zero emissions.
In addition to lower carbon emissions, gas turbines have advanced emission control technologies that reduce the output of harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option for power generation compared to older technologies.
Gas turbine control system
Gas turbine control systems are critical for ensuring the efficient and safe operation of gas turbines, which are extensively used in power generation and various industrial applications. These systems monitor and manage essential parameters such as speed, temperature, fuel flow, and pressure to maintain optimal performance. Utilizing a combination of control hardware, sensors, actuators, and user interfaces, gas turbine control systems employ both closed-loop and open-loop control strategies. Safety features are paramount, with protective controls designed to shut down turbines in hazardous conditions. Recent advancements in digitalization, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring have further enhanced the capabilities of these systems, allowing operators to optimize efficiency and reduce downtime. As technology continues to evolve, gas turbine control systems play a vital role in enhancing performance and reliability across diverse applications, including power generation and aerospace.
The GE gas turbine control system is designed to optimize performance and enhance reliability through advanced monitoring, real-time data analytics, and precise control of key operational parameters. GE offer control and protection systems for both new gas turbine installations and aftermarket retrofits. systems are engineered to meet the rigorous standards for safe and reliable operation across a wide range of units, from small industrial drive systems to cutting-edge advanced-class power generation gas turbines.With a proven history of successful turnkey installations, our turbine control systems enhance unit performance, simplify maintenance processes, and improve operator efficiency. IS200VCMIH2CAA, IS200ECTBG1ABB, IS200EGPAG1BEC are examples of GE control system spare parts.
Challenges in Gas Turbine Adoption
Despite their benefits, there are challenges to wider adoption of gas turbines. High initial costs can be a barrier, particularly for developing countries. Gas turbines also require regular maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently, which can add to the overall cost of ownership.
Additionally, gas turbines face increasing competition from renewable energy sources. As solar and wind technologies become more affordable, they are starting to displace gas turbines in some markets. However, gas turbines’ ability to provide reliable, flexible power means they still have an important role to play, especially in regions where renewables are not yet sufficient to meet demand.
Public perception and policy barriers also pose challenges. As governments and organizations push for more aggressive climate action, the use of any fossil fuel-based technology, including gas turbines, can be viewed as a step backward. It is essential to highlight the role gas turbines play in enabling the transition to a more renewable-focused grid.
Conclusion
Gas turbines are transforming the future of energy production by providing efficient, flexible, and cleaner power solutions. They play a pivotal role in balancing renewable energy sources, reducing carbon emissions, and supporting the transition to a sustainable energy future. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in technology and integration with renewables ensure that gas turbines will continue to be an asset in the energy industry for years to come.

